Multi-instance attention network for few-shot learning
Multi-instance attention network for few-shot learning
Abstract
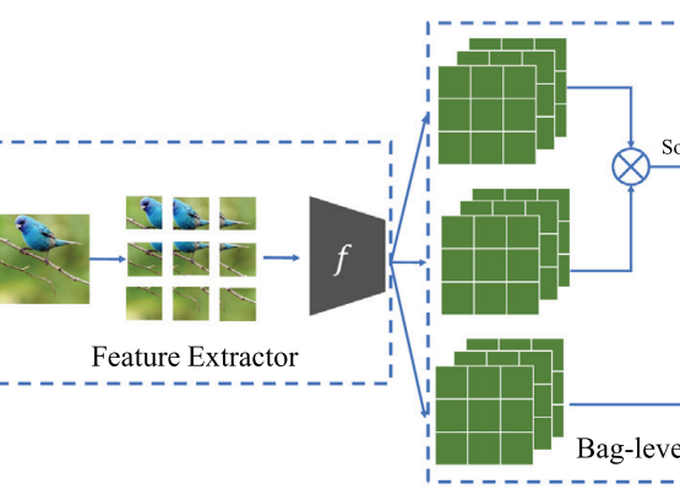
The attention mechanism is usually equipped with a few-shot learning framework and plays a key role in extracting the semantic object(s). However, most attention networks in existing few-shot learning algorithms often work on the channel and/or pixel dimension, leading to the size of attention maps being large. Due to lack of training examples, these attention networks are prone to over-fitting, and may fail to find the semantic target(s). In this paper, we split the original image into patches, extending a new dimension in image data, namely, the patch dimension. On the one hand, the number of patch dimensions is usually much smaller than the traditional three dimensions, thus greatly reducing the number of attention module parameters. On the other hand, the patch dimensional attention mechanism can benefit from multi-instance learning and achieve a good compromise between global and local features. Four comparison experiments on four typical real-world data sets (miniImageNet, tieredImageNet, Fewshot-CIFAR100, Caltech-UCSD Birds-200– 2011) have demonstrated that our proposed algorithm achieves consistent improvement over 6 baseline models (Matching Networks, Relation Networks, Prototypical Networks, MAML, Baseline++, Meta Baseline) and 11 state-of-the-art models (DC, TapNet, SNAIL, TADAM, MetaOptNet, CAN, CTM, DCEM, AFHN, LEO, AWGIM). Our code is available at (https://github.com/rumorgin/MIAN).